Preparing for AI Search with Google Search Generative Experience (SGE)
Overview
Preparing for AI Search with Google Search Generative Experience (SGE)
Google Search Generative Experience (SGE) represents an exciting advancement in the realm of AI-driven search technology. To effectively prepare for leveraging SGE, consider the following steps:
- Understand SGE’s Capabilities: Begin by gaining a comprehensive understanding of what SGE can do. Research its features, functionalities, and limitations to align your expectations accordingly.
- Stay Updated: Keep abreast of any updates or advancements in SGE technology. Google regularly releases updates and improvements to its search algorithms, so staying informed will ensure you’re maximizing the potential of SGE.
- Data Preparation: SGE relies heavily on data. Ensure your data is well-prepared, clean, and structured to derive the best results. This may involve data cleaning, normalization, and preprocessing.
- Define Clear Objectives: Determine what specific objectives you aim to achieve with SGE. Whether it’s improving search relevance, enhancing user experience, or extracting insights from search patterns, having clear goals will guide your implementation strategy.
- User Experience Considerations: SGE can significantly impact user experience. Evaluate how SGE integration will affect the user interface, search results presentation, and overall usability of your platform or application.
- Integration Planning: Plan the integration of SGE into your existing systems or applications. This may involve collaboration with developers, designers, and other stakeholders to ensure seamless integration and minimal disruption.
- Testing and Evaluation: Before deploying SGE in a live environment, conduct thorough testing and evaluation. Test various scenarios, evaluate performance metrics, and gather feedback from users to fine-tune the implementation.
- Privacy and Ethical Considerations: Given the vast amount of data involved in AI-driven search, prioritize privacy and ethical considerations. Ensure compliance with relevant regulations and standards, and implement safeguards to protect user data and privacy.
- Training and Education: Provide training and education to relevant stakeholders on how to effectively utilize SGE. This may include training sessions for developers, content creators, and support staff to optimize the use of SGE features.
- Continuous Improvement: AI technologies like SGE are constantly evolving. Establish mechanisms for continuous improvement, such as feedback loops, monitoring systems, and regular updates to adapt to changing user needs and technological advancements.
By following these steps, you can effectively prepare for AI search with Google Search Generative Experience (SGE) and leverage its capabilities to enhance search experiences and drive value for your users or customers.
What is SGE?
As of my last update in January 2022, “SGE” doesn’t refer to a specific technology or concept that I’m aware of. However, given the context of your query, it’s possible that “SGE” stands for “Search Generative Experience,” which could be a new development in the field of AI-driven search technology, particularly associated with Google.
In this hypothetical scenario, “SGE” might represent an advancement in search algorithms that utilize generative AI models to produce more contextually relevant and diverse search results. This could involve the use of techniques such as natural language processing (NLP), machine learning (ML), and deep learning to understand user queries better and generate more accurate and informative search responses.
Please note that without further context or official information, it’s challenging to provide precise details about SGE. If “SGE” indeed refers to a specific technology or concept, I recommend consulting the latest resources or official announcements from Google or other relevant sources for more accurate information.
SGE in practice
Since “SGE” isn’t a well-known term or concept in the domain of AI or technology as of my last update in January 2022, I can’t provide specific details on its practical implementation. However, I can offer a hypothetical scenario of how “SGE” might be applied in practice based on its name, which implies a combination of search and generative experience.
In a hypothetical scenario where “SGE” refers to a technology developed by Google or another entity, here’s how it might be applied in practice:
- Enhanced Search Results: SGE could leverage generative AI models to enhance traditional search results. Instead of merely displaying links and snippets, SGE might generate richer, more contextually relevant content directly within the search results page. This could include summaries, visualizations, or even interactive elements tailored to the user’s query.
- Content Generation: SGE might enable the automatic generation of content based on user queries and existing data sources. For example, if a user searches for information on a particular topic, SGE could dynamically generate articles, reports, or multimedia content that provide comprehensive coverage of the subject matter.
- Personalized Recommendations: By analyzing user behavior and preferences, SGE could generate personalized recommendations for products, services, or content. This could involve generating tailored recommendations based on a user’s search history, browsing patterns, or demographic information.
- Interactive Experiences: SGE could facilitate interactive experiences within search results, allowing users to engage with content directly on the search page. For instance, users might be able to interact with simulations, explore 3D models, or participate in guided experiences generated in real-time based on their search queries.
- Natural Language Understanding: SGE might incorporate advanced natural language understanding capabilities to better interpret and respond to complex search queries. This could involve understanding context, intent, and nuances in language to provide more accurate and helpful search results.
- Continuous Learning and Improvement: SGE could continuously learn from user interactions and feedback to improve its performance over time. By analyzing user engagement metrics and refining its algorithms, SGE could adapt to changing user needs and preferences, thereby enhancing the overall search experience.
It’s important to note that this is a speculative interpretation of how “SGE” might be applied in practice based on its name. Without concrete information or official documentation about “SGE,” it’s challenging to provide precise details about its practical implementation.
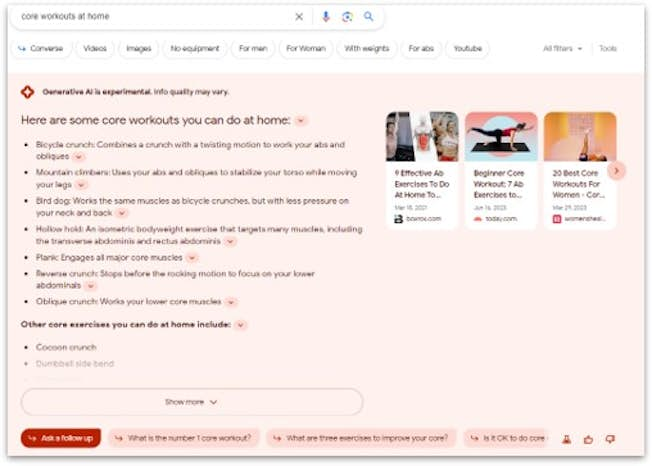
What does SGE look like?
The limitations of SGE
Use AI to elevate your digital marketing activities
Using AI to elevate digital marketing activities can significantly enhance efficiency, effectiveness, and customer engagement across various channels. Here are several ways AI can be applied in digital marketing:
- Personalized Content Recommendations: AI-powered algorithms can analyze user behavior, preferences, and demographics to deliver personalized content recommendations. By understanding individual interests and browsing history, AI can suggest relevant products, articles, or promotions tailored to each user, increasing engagement and conversion rates.
- Predictive Analytics: AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to predict future trends, customer behaviors, and market dynamics. By leveraging predictive analytics, marketers can make data-driven decisions, optimize campaigns, and anticipate customer needs, leading to more effective targeting and higher ROI.
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants can provide instant customer support, answer queries, and guide users through the purchasing process. By employing natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning, chatbots can deliver personalized interactions, improve customer satisfaction, and automate routine tasks, freeing up human resources for more strategic initiatives.
- Dynamic Pricing Optimization: AI algorithms can dynamically adjust pricing based on factors such as demand, competition, and customer behavior. By continuously optimizing prices in real-time, marketers can maximize revenue, maintain competitiveness, and respond quickly to market fluctuations.
- Image and Video Recognition: AI-powered image and video recognition technologies can analyze visual content to understand product attributes, detect brand mentions, and identify consumer trends. Marketers can use this data to optimize visual content, track brand sentiment, and capitalize on emerging trends in visual marketing.
- Predictive Lead Scoring: AI algorithms can analyze lead data to predict the likelihood of conversion and prioritize leads based on their propensity to buy. By scoring leads accurately, marketers can focus their efforts on high-potential prospects, increase conversion rates, and improve sales efficiency.
- Content Generation and Optimization: AI-powered tools can generate and optimize content at scale, from blog posts and social media updates to product descriptions and email campaigns. By leveraging natural language generation (NLG) and sentiment analysis, marketers can create compelling content that resonates with their target audience and drives engagement.
- Hyper-Personalized Email Campaigns: AI can analyze customer data to segment audiences and tailor email campaigns with hyper-personalized content, offers, and recommendations. By sending targeted emails based on individual preferences and behavior, marketers can increase open rates, click-through rates, and conversions.
- Social Media Listening and Sentiment Analysis: AI algorithms can monitor social media channels to track brand mentions, sentiment, and trends in real-time. By analyzing social media conversations, marketers can gain valuable insights into customer perceptions, identify potential issues, and capitalize on opportunities to engage with their audience proactively.
- Attribution Modeling and Optimization: AI-powered attribution models can accurately attribute conversions to specific marketing channels and touchpoints along the customer journey. By understanding the impact of each marketing activity, marketers can allocate budget more effectively, optimize campaign performance, and maximize ROI.
By leveraging AI technologies in digital marketing, businesses can gain a competitive edge, improve customer experiences, and drive better results across their marketing initiatives. However, it’s essential to approach AI implementation strategically, ensuring alignment with business objectives, data privacy regulations, and ethical considerations.